What Types Of Weathering Affects Granite

Frost wedging dissolving and other.
What types of weathering affects granite. Biological activity extreme weather and agents of erosion such as water wind and ice are examples of environmental forces that influences the continuous breakdown wearing away and loosening of rocks and soils. Igneous rocks especially intrusive igneous rocks such as granite weather slowly because it is hard for water to penetrate them. Frost wedging clay formation and other. What types of weathering affect limestone.
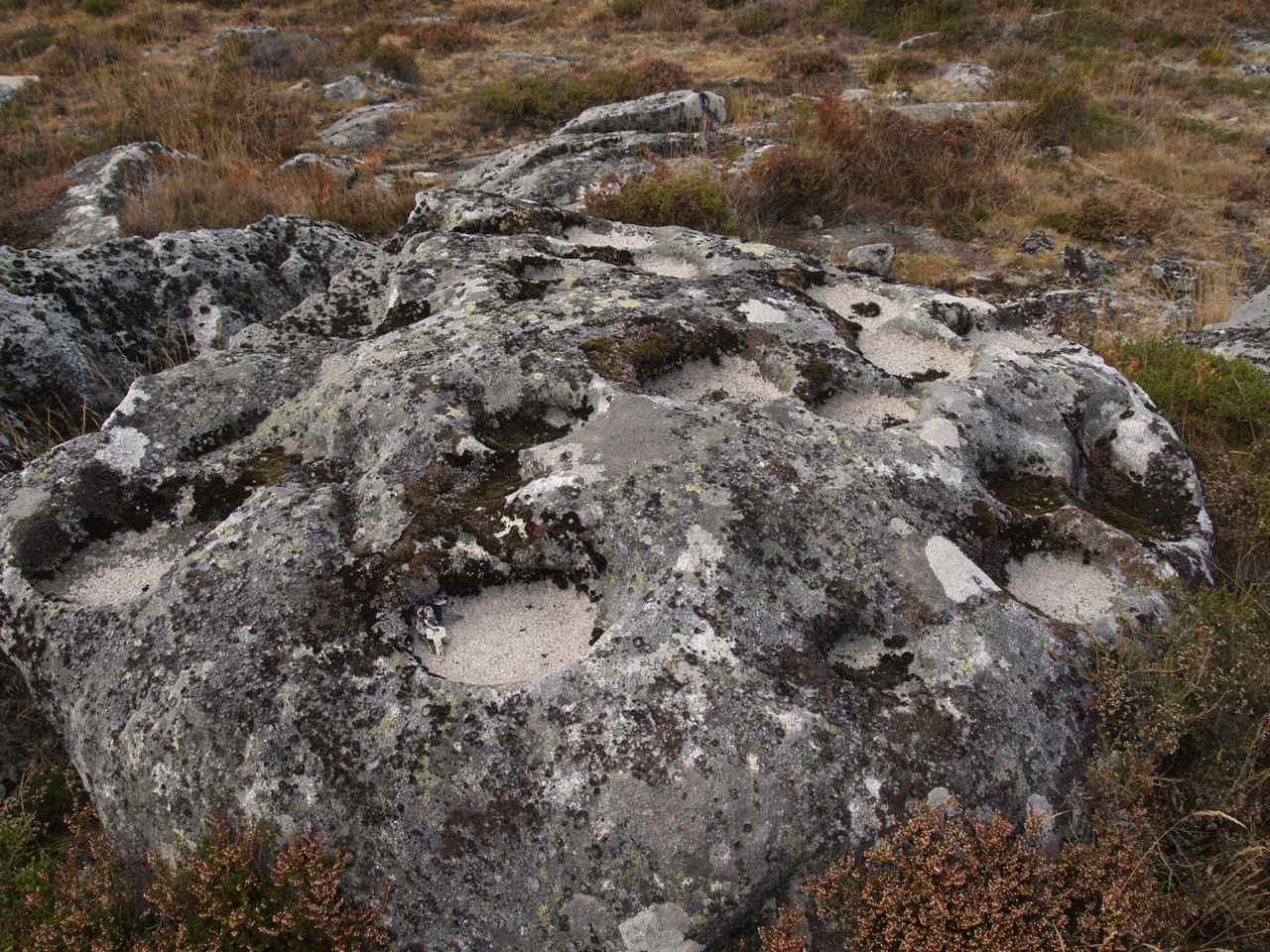
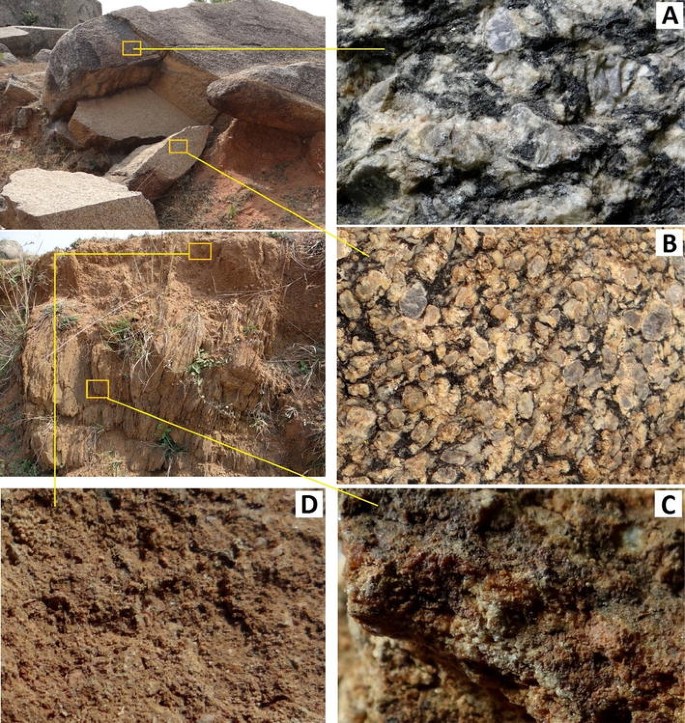
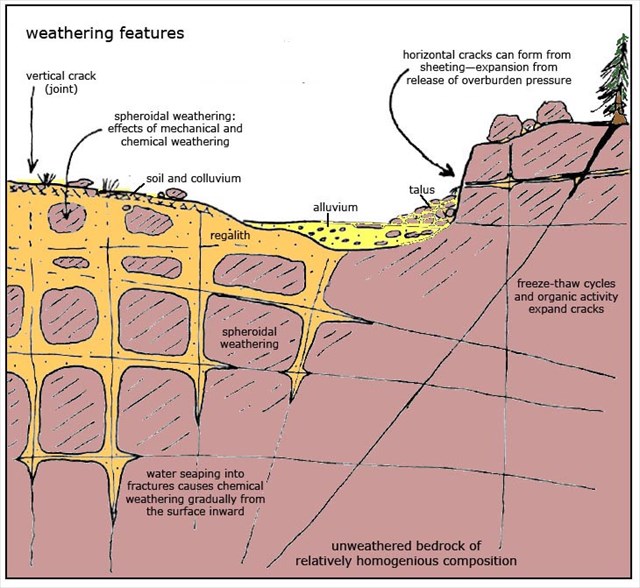
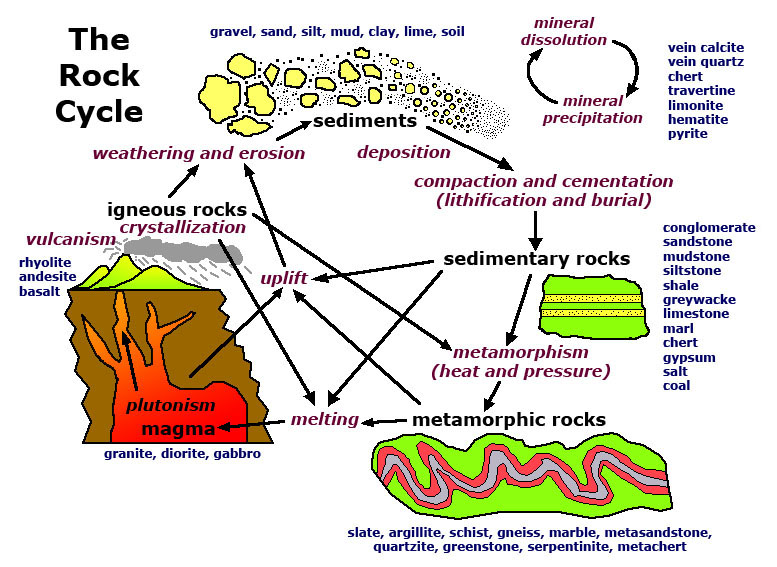
Rocks minerals soils normally change their structure under the action or influence of certain environmental forces. Other types of rock such as limestone are easily weathered because they dissolve in weak acids rocks that resist weathering remain at the surface and form. Massive rocks like granite generally to not contain planes of weakness whereas layered sedimentary rocks have bedding planes that can be easily pulled apart and infiltrated by water. Two of these are types of feldspar a group of silica compounds that constitute the most abundant mineral group on earth.
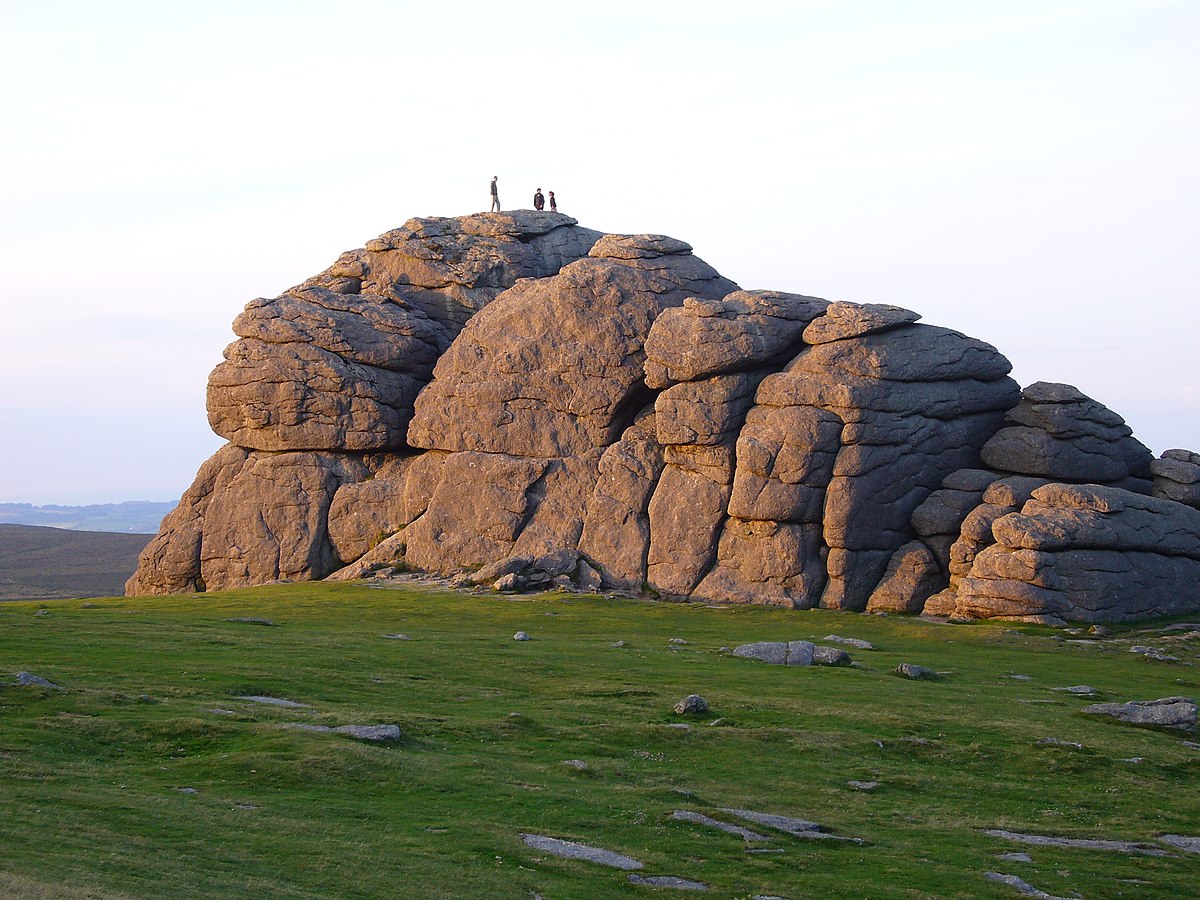
Granite is extremely hard and less affected by the freeze thaw cycle the forces of abrasion and the surface exfoliation processes that are all a part of physical weathering. It consists of four main mineral compounds. A rock s structure also affects its susceptibility to weathering. Certain types of rock are very resistant to weathering.
Granite is extremely resistant and sandstone a little less so due to the percentage of quartz that each rock type contains. What types of weather affect shale. Frost wedging clay formation and other. What types of weathering affect sandstone.
Weathering therefore occurs more slowly in granite than in layered sedimentary rocks. Plagioclase feldspar is a compound of sodium and.