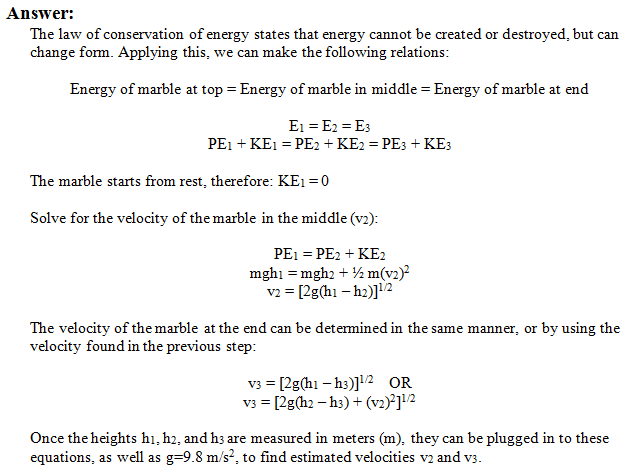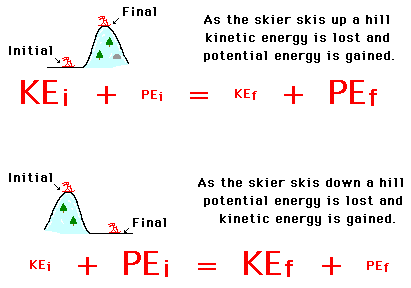What Percentage Of The Marbles Total Kimetic Energy Is Linear

For example if a an object with a mass of 10 kg m 10 kg is moving at a velocity of 5 meters per second v 5 m s the kinetic energy is equal to 125.
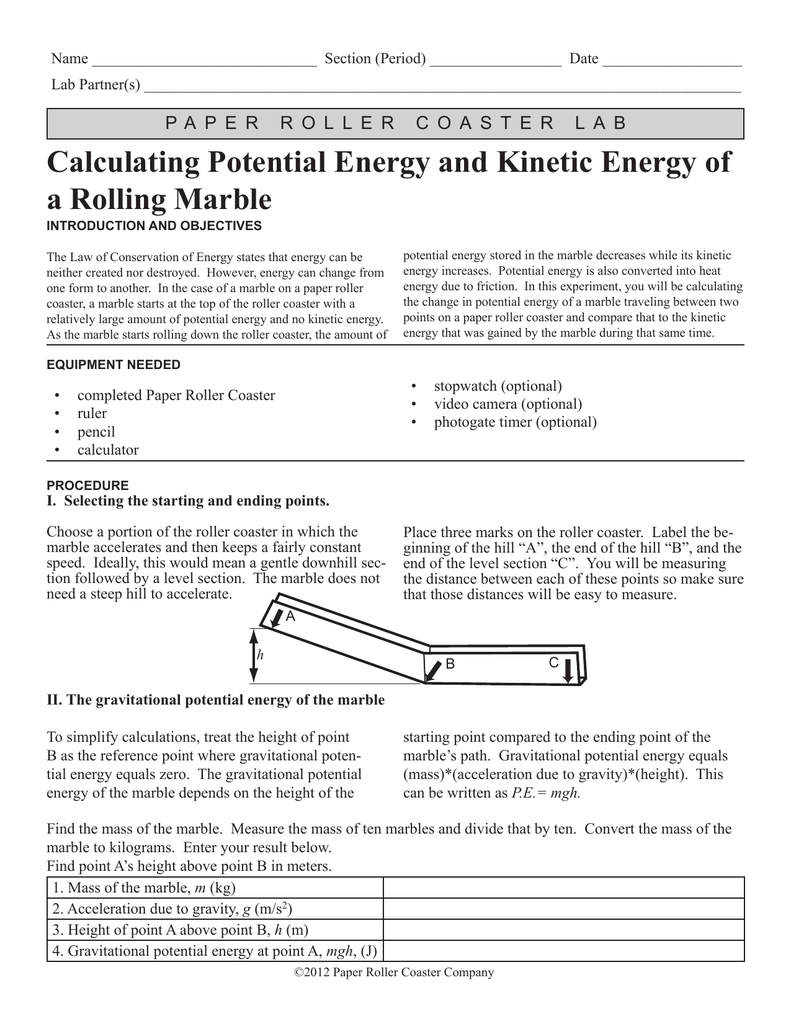
What percentage of the marbles total kimetic energy is linear. Kinetic energy is the energy an object has owing to its motion. When looking only at linear motion you can handle a problem like this by setting the potential energy equal to the final kinetic energy assuming no friction like this. You can calculate the kinetic energy of a body in linear motion with the following equation. Therefore the object weighing 0 1 kg will have a lot more kinetic energy than the object weighing 10 kg for a given momentum p.
There are two ways the kinetic energy will increase if its momentum increases by 25. In fact the kinetic energy of the 0 1 kg object will be 100 times greater than the kinetic energy of the 10 kg object. An increase of 25 means that its mass can have the whole 25 increase as indicated below. The linear speed of the 3 kg mass is v 8 m s and its kinetic energy is mv 2 96 j.
Let k p 2 2m be initial kinetic energy. The sum of the kinetic energies of the three particles is 184 j. The kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion it is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. P is linear momentum and m is mass.
The kinetic energy of a rotating body can be compared to the linear kinetic energy and described in terms of the angular velocity. Then new kinetic energy k 1 2 p 2 2m. The rotational kinetic energy is represented in the following manner for a. An example of potential energy is a stretched out rubber band the farther you stretch it the more potential energy it has.
The extended object s complete kinetic energy is described as the sum of the translational kinetic energy of the centre of mass and rotational kinetic energy of the centre of mass. Since m is in the denominator the kinetic energy is larger for a smaller m with p held constant. The encyclopedia provides the following definition of kinetic energy. Former momentum m v 25 increase of momentum 1 25 m v the ef.
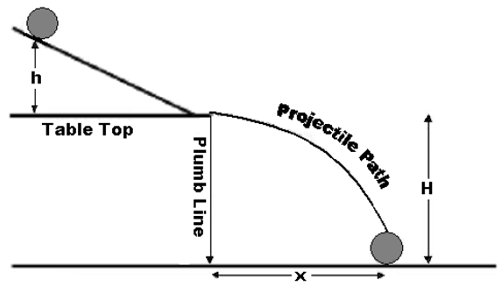
Potential energy is the energy that is stored in an object. Another example is a marble teetering at the top of an inclined plane. Where m is the mass of the object g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height at the top of the ramp. This formula applies to every bit of the object that s rotating each bit of mass has this kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy is the energy of an object in motion. When p is increased by 20 it s new value becomes 1 2 p. Where m is the mass of the object and v is the speed.